Google Map Static Map Upgrade (v2)
Google Map Static Map Upgrade (v2)
New Features Encoded Paths, Polygons & Geocoding
update:
here is a useful tip or two using 'MyMaps' created features:
http://imagine-it.org/google/staticmap/encodemymap.php
(thanks to @pamelafox)
Google have made some changes - many top requested features have been included, but due to these feature requests there are some changes required for you code.
- Locations (in
center,markers, orpathparameters) can now be specified as addresses instead of latitude/longitude coordinates. - Paths can be specified as encoded polylines.
- Paths can be filled and rendered as polygons.
- Colours can now be specified as any 24-bit or 32-bit colour.
Use of the Google Static Maps API is unchangedwith a query limit of 1000 unique (different) image requests per viewer per day
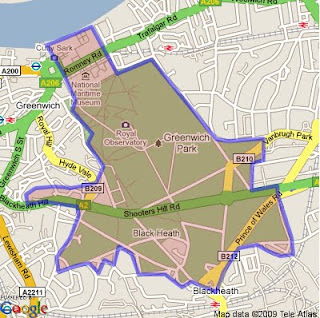
encoded polygon in Google Static Maps v2
http://maps.google.com/maps/api/staticmap?size=400x400&path=fillcolor:0xAA000033|color:0000ff|enc:ykfyHln@bBtLhJkI|JyGdChAzHiL
|BfBvH}IlEvCl@tG%60@rGYjIXbLpApEbC_@a@kJ~@cUpB_@tH~D~FzG%60Eg@
qAeK[iGvBgEeDwB%60A}EuFwA|AqGvG_D?_QdDiJgAiElCuOkGuC_I_Is@iK|
AuFz@_GYuGuEj@{PtG_CTbA~OsJKa@sFcH?XrVQhGi%60@dj@zDdVwRdPrCbO
&key=YOUR API KEY&sensor=false
Note: The fastest way to create an encoded polygon is to create a polygon in Google Earth then right click the polygon and copy & paste into this site
http://facstaff.unca.edu/mcmcclur/GoogleMaps/EncodePolyline/encodeForm.html
check your polygon is located correctly. The click then 'Show Code'
The line
{points:contains the encoded polygon. use this for your static map.
Having been re-written The Static Maps API v2 changes are:
red=old green=new
-
Instead of specifying
maptype=mobile, specify the desired map type (likemaptype=hybrid) and the parametermobile=true. This way, we can provide mobile optimised tiles for every map type. -
The colour for a path is now specified using
"color", not"rgba":For example:
&path=rgba:0x0000FF80,weight:5|37.40303,-122.08334|37.39471,-122.07201|37.40589,-122.06171
becomes:&path=color:0x0000FF80|weight:5|37.40303,-122.08334|37.39471,-122.07201|37.40589,-122.06171 -
Similar to how the path styles were specified before, the marker styles are now specified using
key:valuepairs, separated by pipes [|]. Marker labels are now denoted using uppercase alpha characters instead of lowercase alpha characters.For example:
midreda
becomes:size:mid|color:red|label:A -
Instead of specifying the marker style after each marker parameter, specify the style at the beginning of the
markers=parameter, and that style will apply to all of the markers proceeding. If you want to show markers with different styles, just supply a newmarkers=parameter for each one.For example:
markers=37.400465,-122.073003,midreda|37.437328,-122.159928,midreda|37.369110,-122.096034,smallblue
becomes:markers=size:mid|color:red|label:E|37.400465,-122.073003|37.437328,-122.159928&markers=size:small|color:blue|37.369110,-122.096034 -
Marker labels now require uppercase alphanumeric characters in the
labelparameter. This will allow us to later supply lowercase characters if we wish.For example:
markers=37.400465,-122.073003,midreda
becomes:markers=size:mid|color:red|label:E|37.400465,-122.073003 -
Instead of using the
span=parameter to make sure that your static map shows a particular viewport, use thevisible=parameter instead, and specify a list of coordinates that must be shown.For example:
center=0,0&span=20,20
becomes:visible=10,-10|-10,10 -
The
frameparameter is no longer supported.
After upgrading your existing functionality, you might be interested in adding some of the new API functionality to your website.
Tools: Make A Static Map Wizard (V2)
http://gmaps-samples.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/simplewizard/makestaticmap.html
Source:
Labels: Encoded, Geocoding, Google, Map, Polygons, Static, Upgrade, v2